MedicationPrescription-v1.0.1(2015EN)
General information
Name: nl.nfu.MedicationPrescription ![]()
Version: 1.0.1
HCIM Status:Final
Release: 2015
Release status: Published
Release date: 1-4-2015
Metadata
| DCM::CoderList | Kerngroep Registratie aan de Bron |
| DCM::ContactInformation.Address | |
| DCM::ContactInformation.Name | * |
| DCM::ContactInformation.Telecom | |
| DCM::ContentAuthorList | Projectgroep Generieke Overdrachtsgegevens & Kerngroep Registratie aan de Bron |
| DCM::CreationDate | 19-12-2013 |
| DCM::DeprecatedDate | |
| DCM::DescriptionLanguage | nl |
| DCM::EndorsingAuthority.Address | |
| DCM::EndorsingAuthority.Name | NFU |
| DCM::EndorsingAuthority.Telecom | |
| DCM::Id | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.3.9.5 |
| DCM::KeywordList | Medicatie, Voorschrift |
| DCM::LifecycleStatus | Final |
| DCM::ModelerList | Kerngroep Registratie aan de Bron |
| DCM::Name | nl.nfu.MedicatieVoorschrift |
| DCM::PublicationDate | 1-4-2015 |
| DCM::PublicationStatus | Published |
| DCM::ReviewerList | Projectgroep Generieke Overdrachtsgegevens & Kerngroep Registratie aan de Bron |
| DCM::RevisionDate | 22-5-2015 |
| DCM::Superseeds | nl.nfu.OverdrachtMedicatie-v1.1 (2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.3.9.1) |
| DCM::Version | 1.0.1 |
| HCIM::PublicationLanguage | EN |
Revision History
Only available in Dutch
Publicatieversie 1.0 (01-04-2015)
| ZIB-56 | RFC Bouwsteen Medicatie |
| ZIB-78 | Medicatie, diverse issues |
| ZIB-80 | OverdrachtMedicatie v1.1 |
| ZIB-144 | Aanpassingen in SNOMED CT codes en omschrijvingen voor codelijst DagdeelCodelijst n.a.v. review terminologie expert. |
| ZIB-145 | Aanpassingen in SNOMED CT codes en omschrijvingen voor codelijst WeekdagenCodelijst n.a.v. review terminologie expert. |
| ZIB-308 | Prefix Overdracht weggehaald bij de generieke bouwstenen |
| ZIB-353 | Tagged values DCM::CodeSystem aanpassen naar DCM::ValueSet incl. gekoppelde codelijst. |
Incl. algemene wijzigingsverzoeken:
| ZIB-94 | Aanpassen tekst van Disclaimer, Terms of Use & Copyrights |
| ZIB-154 | Consequenties opsplitsing Medicatie bouwstenen voor overige bouwstenen. |
| ZIB-200 | Naamgeving SNOMED CT in tagged values klinische bouwstenen gelijk getrokken. |
| ZIB-201 | Naamgeving OID: in tagged value notes van klinische bouwstenen gelijk getrokken. |
| ZIB-309 | EOI aangepast |
| ZIB-324 | Codelijsten Name en Description beginnen met een Hoofdletter |
| ZIB-326 | Tekstuele aanpassingen conform de kwaliteitsreview kerngroep 2015 |
Publicatieversie 1.0.1 (22-05-2015)
| ZIB-393 | Tagged value DCM::LifecycleStatus bevat waarde Draft. |
| ZIB-390 | De OID van de codelijst WeekdagenCodelijst van het concept Weekdagen is onjuist in de onderliggende codelijst. |
| ZIB-377 | Source/Destination van MaximumAantalPertijd en Criterium richting ZoNodig aanpassen. |
| ZIB-376 | Inconsistent gebruik van naamgeving Ing(r)edientCodeGTINCodelijst. |
| ZIB-372 | Concepten Mantelzorger::Contactpersoon en Toelichting uit nl.nfu.Voorschrift-v1.0 hebben hetzelfde ID. |
Concept
A medication prescription is an agreement or order for the use of medication in which the following are described: the prescribed product, instructions for use or administration and (optionally) a request for delivery.
The dose information is given for every prescribed product: the start date and time, and if possible stop date and time or total number of administrations, administering schedule (frequency or interval, administering times, link with meals etc.), the number of doses, administering speed or time (for drips), and the route of administration.
An indication can also be included of whether the medication is only to be administered ‘as needed’ and under which conditions the product is to be used, and how high the agreed maximum dose is in a certain period.
If possible, the reason or indication of starting/stopping/changes in use is to be included.
Medication that has been discontinued temporarily can be included as well.
If the prescription also contains the order to provide a product to a patient or to an administerer, it can officially be referred to as a prescription.
Purpose
The goal of the medication prescription is to provide insight in the therapeutic intention of the healthcare provider in terms of treatment with medicines. Furthermore, it offers the option to record any requests asking the provider of the medication to provide medication to the patient.
Evidence Base
Content-wise, the building block was made to support the national medication transfer guidelines (www.medicatieoverdracht.nl). The appendices to the guidelines describe how the structure can depend on the healthcare providers involved, the local situation and the existing preconditions. The concept guidelines provide sufficient space for this. That means that the collaborating healthcare providers draw up their own protocol, applicable to their specific situation. In other words, information details in transfers within the second line may differ from those in transfers between the first and second line, or between healthcare providers and pharmacies.
Where possible, coding within the Medication domain is based on the G standard (managed by the firm Z-index). This is because in the Netherlands, almost all software packages for electronic prescriptions, pharmacy management and medication monitoring are based on this standard. The content of the G standard is very precisely updated under the direction of the KNMP in consultation with stakeholders, including the software suppliers.
The following were taken into account in determining restrictions and instructions on information domains (value sets) to be used:
- Implementation Guidelines HL7 v3 medication information
- Data set Medication process
The results of the ‘G standard platform’ consultations between users and developers of the G standard and content experts were taken into account as well.
The information model for medication is very extensive. In simple implementations, the following are of primary importance:
- the correct product name and coding
- medication use (patient information)
- the instructions, which can take the form of a prescription (with agreements on use and requests to supply the medication) or a medication order (only administering instructions)
- dosage instructions with the route of administration, dose per administration, period of use (start and stop date), dose schedule and other administering instructions
- the reason for prescription (prescriber information) or reason for use (patient information)
- the status (active, interrupted, discontinued or completed)
Information Model
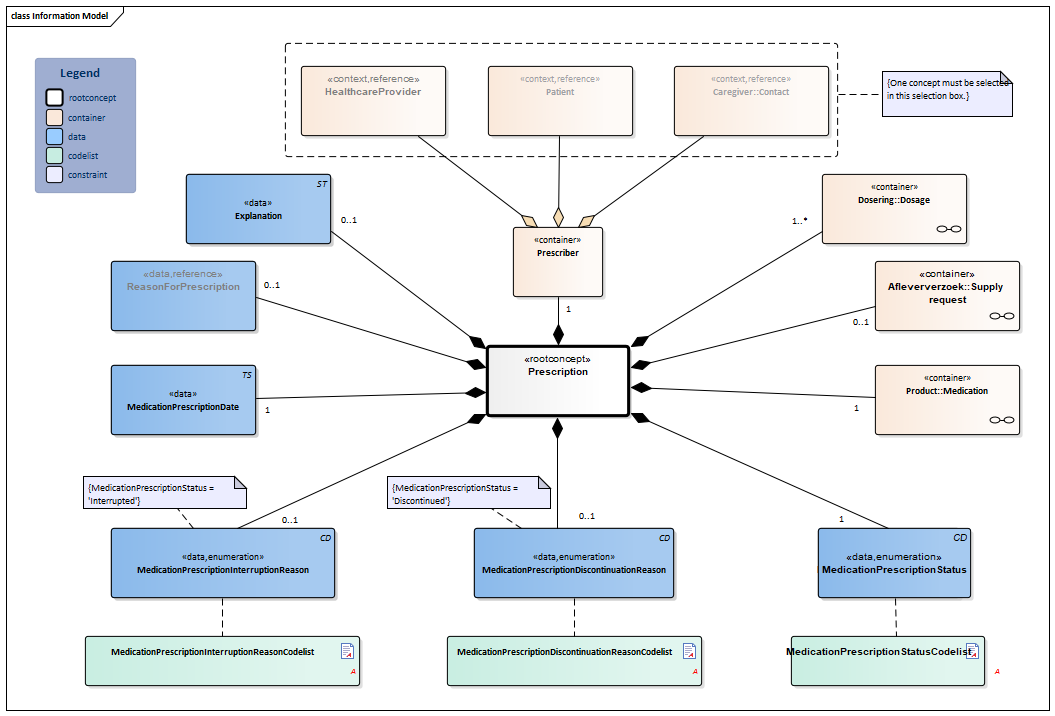
| Type | Id | Concept | Card. | Definition | DefinitionCode | Reference | |||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.1 | Root concept of the MedicationPrescription building block. This root concept contains all data elements of the MedicationPrescription building block. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
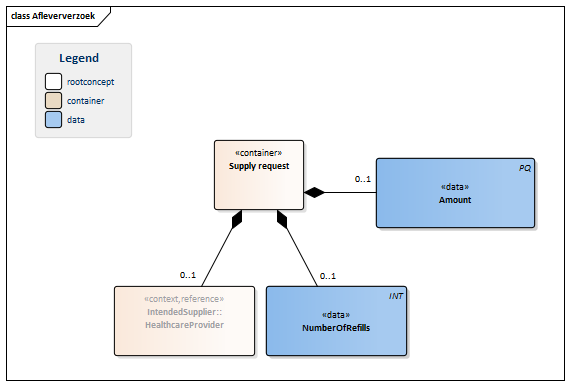
| NL-CM:9.5.5 | 0..1 | Container of the SupplyRequest concept. This container contains all data elements of the SupplyRequest concept.
The supply request is the order placed with the supplier to supply medication. The number of refills can be indicated as well. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.30 | 0..1 | The amount to be supplied defines the number of units of the ordered product that have to be supplied. The amount is given in the unit of the ordered product. The amount to be supplied is always the amount per partial supply. The number of refills indicates how often this amount is allowed to be supplied. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.31 | 0..1 | Maximum number of partial supplies (refills) allowed to be given for this prescription. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.32 | 0..1 | In almost all cases, the intended supplier will be a registered pharmacist. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
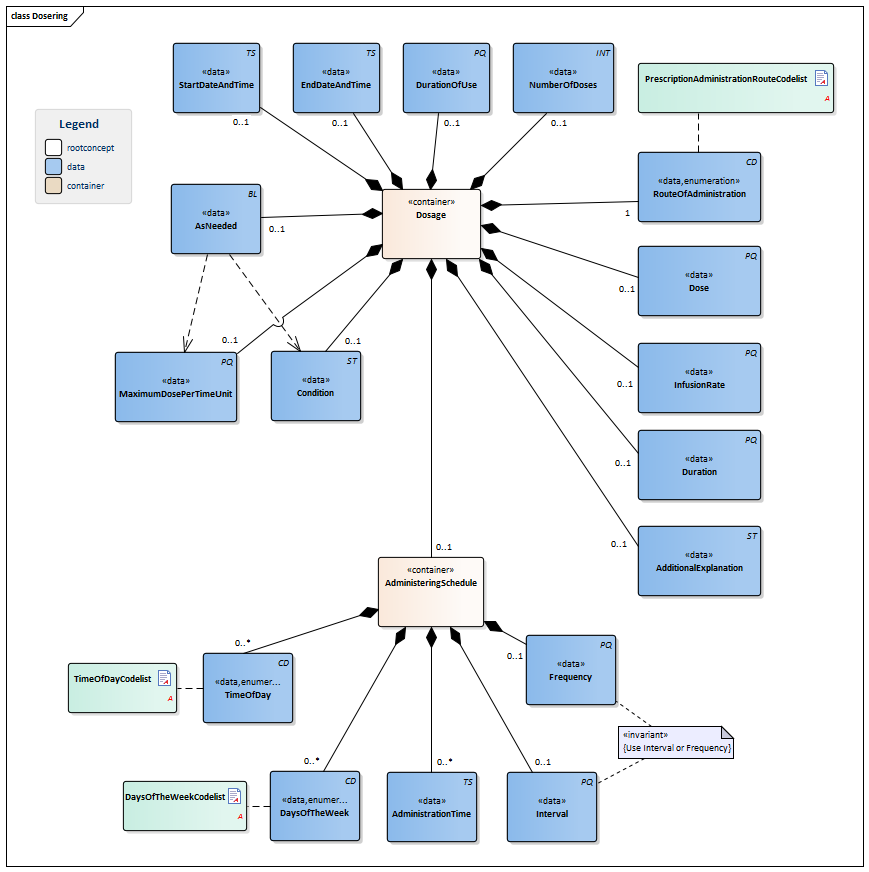
| NL-CM:9.5.4 | 1..* | Container of the Dosage concept. This container contains all data elements of the Dosage concept.
Instructions for the administerer to administer the medication (the patient themselves, a nurse or other aid). When taking stock of medication use, the dosage describes the pattern of use established by the patient. If the dose schedule (distribution of doses over time) and the dose per administration have been determined, there will be a single instruction for use. Multiple parallel instructions for use can be included in the event of a changing dose within one day and in the event of a variable frequency of use. Multiple sequential instructions for use can be included in the event of changing doses within one period and/or in the event of a changing dose schedule. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.11 | 0..1 | The date (and time) at which use of the product started or will start according to the dose information. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.12 | 0..1 | The end date of a dose (specification of use). This can be an agreed date, but also the date on which use of the product was discontinued (stop date, discontinuation date). | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.13 | 0..1 | In some cases, it may be necessary to indicate the intended duration of use, which cannot be calculated from the start date, end date and/or total number of doses. This could for example be the case with temporary sleep medication to be taken as needed. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.14 | 0..1 | In many cases, the total number of doses indicates the desired duration of use. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.15 | 0..1 | The administration dose indicates the dose amount per administration.
The dosage is described in the unit accompanying the product; usually, this is just a number of units or doses. Liquids and other divisible products will usually include a unit of volume (preferably "ml"). In many cases, the prescriber will want to indicate the dose in units of weight of the active substance. If only the substance is included and not the product, the amount of that substance will be given. Paracetamol 1000mg is equivalent to 2 Paracetamol 500mg tablets (or units). The dosage is sometimes given as a calculation, in which the patient’s body weight or body surface area is often used as a parameter. The calculation is however no more than an aid in reaching a decision. In the event of constant administration, sometimes the dose per administration (e.g. 20ml in a syringe or 500ml in a bag) is given in addition to the administration speed (rate of infusion), but it is often also omitted. A general dosage recommendation such as ‘Use according to protocol’ or ‘See instructions’ can be sufficient. In that case, no dose per administration is given either. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.16 | 1 | The route through which the medication is to be administered (oral, nasal, intravenous,...). |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.17 | 0..1 | The rate of infusion is used in slow administration of liquids. In practice, the measuring unit is almost always ml/hour.
Entering an interval (such as 0-10 ml/hour) is also a commonly used option. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.18 | 0..1 | The duration of administration indicates how long the medication is to be administered and used in the event of slow administration of liquids. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.19 | 0..1 | The additional explanation contains extra information on the use of or considerations for the current prescription.
This can also include all instructions for use. The text can come from the original "paper" medication prescription, but can also be generated from the coded information. This concept may contain more information than what is structurally coded in the information below, but may not conflict with it. The instructions may not conflict with other components of the request for administration. The instructions can also refer to an existing protocol. The G standard contains many texts that can support this attribute, in for example G standard table 362, which contains texts from the general practitioners’ standard WCIA table 25. If desired, these texts can be used to structure this concept. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.20 | 0..1 | The condition for administering medication can be:
Such a criterion will be entered in correspondence with the AsNeeded indicator. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.21 | 0..1 | The MaximumAmountPerPeriod concept indicates the maximum duration a product can be used with an 'as needed' prescription. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.22 | 0..1 | Indicates whether the dose is only to be administered under certain conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.23 | 0..1 | Container of the AdministeringSchedule concept. This container contains all data elements of the AdministeringSchedule concept.
Specifications of the times at which the medication is administered/is to be administered. This is indicated as follows:
If a certain medication is not to be taken daily, the aforementioned can be combined with daily indications:
The specified administration "infinite" will automatically be repeated until:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.24 | 0..1 | The frequency indicates the number of dose moments per time unit, usually per day. If this frequency is included, then the Interval will not have been included.
In that case, a reasonable distribution throughout the day is expected, but exact times are not given. This is left to the patient. It is the most common type of extramural prescription. In the case of Baxter packs and intramural care, such a prescription is used to draw up a (location-specific) outline for distribution times (logistics). |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.25 | 0..1 | Interval indicates the time between dose times. If this is included, the Frequency will not have been included.
Examples: every 4 hours, every 3 weeks. The times can now be chosen freely, but distribution throughout the day is more precise, and the interval between times is important (e.g. in the case of antibiotics) In the case of Baxter packs and intramural care, such a prescription is used to draw up a (location-specific) outline for distribution times (logistics). |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.26 | 0..* | The time of administration is a specific time of day (on the clock). This time usually isn’t (intended to be) exact. There can be multiple administering times in one day.
The intended time of administration can also be entered as a time of day (morning, afternoon, evening, night-time). The administration time is then to be left empty, and the time of day can be entered in the TimeOfDay concept. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.27 | 0..* | DaysOfTheWeek indicates a pattern of doses on fixed days of the week. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.28 | 0..* | To make prescriptions easier for the patient and to facilitate transfers between first and second line, it is best to indicate a time of day instead of a set time.
To code a time of day in the administering schedule, agreements were made between the first and second line to be able to clearly translate the first-line WCIA 21 code to standard times of day in clinical second-line medication assignments. In this process, the following times of day apply: WCIA Second line morning 6:00am - 12:00pm afternoon 12:00pm - 6:00pm evening 6:00pm - 12:00am night-time 12:00am - 6:00am |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
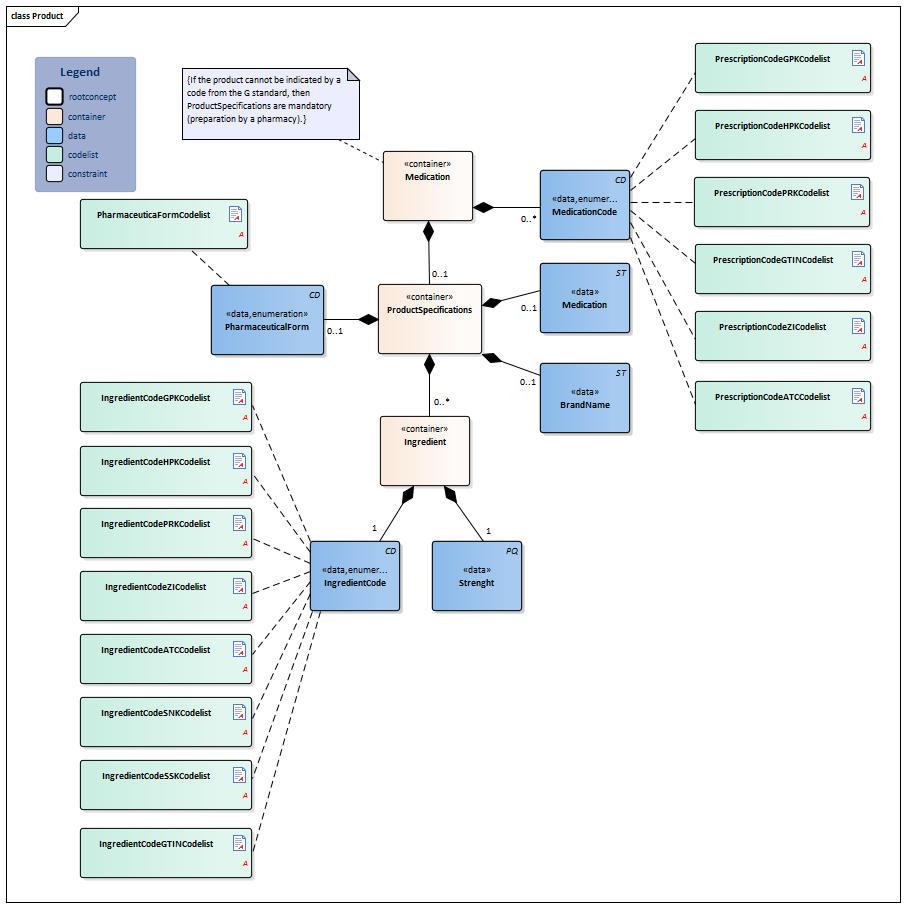
| NL-CM:9.5.6 | 1 | Container of the Product concept. This container contains all data elements of the Product concept.
The prescribed product is usually a medicine. However, medical aids and bandages can also be prescribed and supplied via the pharmacy. Strictly speaking, food and blood products do not belong in the medication category, but can be prescribed and supplied by a pharmacy as well. A type of medication can be indicated with a single code. That code can be chosen from several possible coding systems (concretely: GPK, PRK, HPK or article numbers). Correct use of these codes in the software systems will sufficiently record the composition of the product used, making a complete product specification unnecessary. In addition to a primary code, alternative codes from other coding systems can also be entered (so that the GPK can be sent along in the event that the patient was registered based on PRK, for example). Entering multiple ingredients will enable you to display a compound product. If one of the composite parts is liquid, the dosage will be given in milliliters; otherwise it will be given in ‘units’. In that case, the composition of the medication can be specified implicitly (with the use of a medication code) or explicitly, for example by listing the (active) substance(s) of the medication. Prescriptions to be prepared by the pharmacy can be entered as well. This can be done by means of the option listed above to enter coded ingredients and/or by entering the composition and preparation method as free text. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.33 | 0..* | Coding medication in the Netherlands is done on the basis of the G standard (issued by Z-index), which is filled under the direction of KNMP.
The coded medication can be expressed as:
The GTIN enables identification of the product including its origin with a barcode. The ATKODE is the number with which wholesalers link the article to pharmacy systems (e.g. a box with 3 strips of 10 tablets). The HPK is the code for the trade product (with the brand name) as used per dose/per time the medication is taken (1 pill, 1 puff, 1ml) The PRK codes for the same product as the HPK does, but is not linked to a manufacturer (no brand name, no characteristics such as color, geometrical shape etc.). This code will enable a generic prescription, while still defining which trade product can be taken (e.g. a 200ml bag). The generic product code defines the composition of a product, and is sufficient for recording the prescription, but not the order. The prescription code (PRK) was developed and added to the older generic (GPK) and supplier-specific (HPK, ATKODE) coding to enable a generic product to be entered without listing a specific brand on the one hand, and to enable providing enough information to support the pharmacy supplying it on the other. The GTIN coding is used for the implementation of a barcode scanning standard and to be able to trace the origin of the product. The 90.000.000 number is used in accordance with national agreements. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.34 | 0..1 | Container of the ProductSpecifications concept. This container contains all data elements of the ProductSpecifications concept.
Product specifications are required if the product code is not sufficient to ascertain the active substances and strength. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.35 | 0..1 | There is no code for medication entered in free text. In these cases, enter the complete description. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.36 | 0..1 | If the ProductCode does not contain a brand name, the brand name can be entered in this concept. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.37 | 0..1 | The pharmaceutical form indicates the form of the medication in accordance with the route of administration. Examples include: tablet, suppository, infusion liquid, ointment. If the product has a generic code in the G standard, the form will be known in the G standard. For products without a code (free text, preparation by the pharmacy), the means of administration can be entered. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.38 | 0..* | Container of the Ingredient concept. This container contains all data elements of the Ingredient concept.
A product contains one or more active substances and excipients. These are usually determined by the product code. For medication prepared or compounded by the local pharmacy, each ingredient must be entered separately. The active substances play an important role, as they: a) determine the pharmacotherapeutic effect of the medication and b) serve as the basis for the indication of the strength of the medication (e.g. 200mg). |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.39 | 1 | The amount of absorbed active substance or addition per unit of product. This could be a concentration if the medication is dissolved in liquid, for example. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.40 | 1 | Active substance or excipient.
Here, the same codes can be used as for the ProductCode (for dilutions and compounds in particular), but now, the ATC, SSK and SNK codes can also be used to indicate a substance (to list ingredients of local products prepared by the pharmacy).
The ATC is an international classification of pharmaceutical substances without a reference to specific products on the market. Therefore, the ATC code of a generic product will not contain a reference to a certain dose, pharmaceutical form or route of administration; it will only contain a reference to the ingredients (not the amount/concentration/strength). |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.7 | 1 | The MedicationPrescriptionStatus indicates whether the prescription is actively used, temporarily interrupted, or by now discontinued. The status describes the consecutive stages of the prescription process and is important for the indication of the schedule for use.
Interrupting (home) use often occurs in the event of admittance to a healthcare facility, prior to a procedure and in response to monitoring (level determination, effect measurements, etc.). When documenting this, the following interpretations are used:
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.8 | 0..1 | Reason for discontinuing the use of a certain medicine. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.9 | 0..1 | Reason for interrupting the use of a certain medicine. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.10 | 1 | Date on which the prescription was issued. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.2 | 0..1 | The medical reason for the prescription or for use of the medication. This can be used to enter a medical indication which was the direct cause for prescription or for use of the medication in question.
It can concern every type of problem (or condition) of the patient, almost always a diagnosis, complaint or symptom. Please note: The BST401T file of the G standard contains a "special reference" to indicate that "exchange of the reason for prescription is essential". |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.41 | 1 | Container of the Prescriber concept. This container contains all data elements of the Prescriber concept.
The person who prescribed the prescription. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.3 | (0..1) | The healthcare provider responsible for the prescription. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.42 | (0..1) | The patient who prescribed their own product. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.43 | (0..1) | The caregiver who prescribed the product. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| NL-CM:9.5.44 | 0..1 | Comments on the medication prescription. | |||||||||||||||||||||
Columns Concept and DefinitionCode: hover over the values for more information
For explanation of the symbols, please see the legend page ![]()
Example Instances
Only available in Dutch
| DatumMedicatieVoorschrift | Product | Dosering | Voorschrijver | Medicatie VoorschriftStatus |
MedicatieReden VanOnderbreken | |||
| ProductNaam | StartDatum | Toedieningsschema | ToedieningsWeg | Keerdosis | Zorgverlener | |||
| Frequentie | Naamgegevens | |||||||
| 18-09-2012 | Carbasalaatcalcium poeder 100mg | 18-09-2012 | 1x/dag | Oraal | 100mg (=1st) | C. Dols | Onderbroken | Geplande ingreep |
| DatumMedicatieVoorschrift | Product | Dosering | Voorschrijver | Medicatie VoorschriftStatus |
RedenVan Voorschrijven | |||
| ProductNaam | StartDatum | Toedieningsschema | ToedieningsWeg | Keerdosis | Zorgverlener | ProbleemNaam | ||
| Frequentie | Weekdagen | Toedientijd | Naamgegevens | |||||||
| 01-03-2012 | Methotrexaat invlst 25mg/ml amp 2ml | 01-03-2012 | 1x/wk op maandag(14u) | iv | 50mg (=2ml) | B. Takken | Actief | Autoimmuunziekte |
References
1. GROOT, E. (2011) Dataset medicatieproces 2011. [Online] Den Haag: Nictiz. Beschikbaar op: http://www.nictiz.nl/module/360/590/Dataset_Medicatieproces_2011.xlsx [Geraadpleegd: 23 juli 2014].
2. HL7v3-implementatiehandleiding medicatieproces versie 6.1.0.0. [Online] Den Haag: Nictiz. Beschikbaar op: http://www.nictiz.nl/uploaded/FILES/html_cabinet/live/Zorgtoepassing/Medicatieproces/AORTA_Mp_IH_Medicatieproces_HL7.htm [Geraadpleegd: 23 juli 2014].
3. Dossier Medicatieoverzicht. [Online] Beschikbaar op: Oria.nl. [Geraadpleegd: 23 juli 2014].
4. G-standaard documentatie. [Online] Beschikbaar op: http://www.z-index.nl/ [Geraadpleegd: 23 juli 2014].
Valuesets
DaysOfTheWeekCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.4 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Conceptcode | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID | Description |
| Monday | 307145004 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | maandag |
| Tuesday | 307147007 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | dinsdag |
| Wednesday | 307148002 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | woensdag |
| Thursday | 307149005 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | donderdag |
| Friday | 307150005 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | vrijdag |
| Saturday | 307151009 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | zaterdag |
| Sunday | 307146003 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | zondag |
IngredientCodeATCCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.14 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | Anatomic Therapeutic Classification (ATC) | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.73 |
IngredientCodeGPKCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.16 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-Standaard Generieke Product Kode (GPK) | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.1 |
IngredientCodeGTINCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.21 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) | 1.3.160 |
IngredientCodeHPKCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.17 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-Standaard Handels Product Kode (HPK) | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.7 |
IngredientCodePRKCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.18 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-Standaard Voorschrijfproducten (PRK) | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.10 |
IngredientCodeSNKCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.15 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-standaard Stofnaamcode (SNK) | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.1.750 |
IngredientCodeSSKCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.19 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-standaard Stofnaamcode i.c.m. toedieningsweg (SSK) | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.1.725 |
IngredientCodeZICodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.12 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-Standaard Artikelen (ook KNMP-nummer, ATKODE) | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.8 |
MedicationPrescriptionDiscontinuationReasonCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.2 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Conceptcode | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID | Description |
| Intolerance | SINTOL | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Bijwerking, allergie of intolerantie |
| Condition alert [Proposed therapy may be inappropriate or contraindicated due to an existing/recent patient condition or diagnosis] | COND | ActCode | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.4 | Contra-indicatie [comorbiditeit, diagnose] |
| Drug interacts with another drug | SDDI | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Interactie [interactie met ander medicament met hogere urgentie] |
| Dose change | DOSECHG | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Dosiswijziging |
| No longer required for treatment | NOREQ | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Niet langer vereist voor de behandeling [indicatie vervallen] |
| Ineffective | INEFFECT | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Niet effectief |
| Formulary policy | FP | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Ander voorschrijfbeleid |
| Product discontinued | DISCONT | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Product niet meer leverbaar |
| Not covered | NOTCOVER | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Product wordt niet vergoed |
| Patient request | PAT | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Informatie of wens patiënt |
MedicationPrescriptionInterruptionReasonCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.3 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Conceptcode | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID | Description |
| Drug level too high | DRUGHIGH | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Te hoge geneesmiddel spiegel |
| Lab interference issues | LABINT | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Interferentie met gepland labonderzoek |
| Parent is pregnant/breast feeding | PREG | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Zwangerschap of borstvoeding |
| Patient not-available | NON-AVAIL | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Patiënt is tijdelijk afwezig of ondergaat ingreep |
| Response to monitoring | MONIT | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Reactie op monitoring |
| Drug interacts with another drug | SDDI | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Interactie met ander medicament met hogere urgentie |
| Duplicate therapy | SDUPTHER | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Een andere therapie maakt het gebruik tijdelijk overbodig |
| Patient scheduled for surgery | SURG | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Geplande ingreep |
| Waiting for old drug to wash out | WASHOUT | ActReason | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.8 | Tijdelijk onderbreken tot ander geneesmiddel geen werking meer uitoefent |
MedicationPrescriptionStatusCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.1 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Conceptcode | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID | Description |
| Active | active | ActStatus | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.14 | Actief |
| Suspended | suspended | ActStatus | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.14 | Onderbroken |
| Aborted | aborted | ActStatus | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.14 | Afgebroken |
| Completed | completed | ActStatus | 2.16.840.1.113883.5.14 | Voltooid |
PharmaceuticaFormCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.7 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-Standaard Farmaceutische vormen | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.11 |
PrescriptionAdministrationRouteCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.6 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-Standaard Toedieningswegen | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.9 |
PrescriptionCodeATCCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.20 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | Anatomic Therapeutic Classification (ATC) | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.73 |
PrescriptionCodeGPKCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.8 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-Standaard Generieke Product Kode (GPK) | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.1 |
PrescriptionCodeGTINCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.11 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) | 1.3.160 |
PrescriptionCodeHPKCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.9 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-Standaard Handels Product Kode (HPK) | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.7 |
PrescriptionCodePRKCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.10 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-Standaard Voorschrijfproducten (PRK) | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.10 |
PrescriptionCodeZICodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.13 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID |
| Alle waarden | G-Standaard Artikelen (ook KNMP-nummer, ATKODE) | 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.4.8 |
TimeOfDayCodelist
| Valueset OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.2.4.3.11.60.40.2.9.5.5 | Binding: |
| Conceptname | Conceptcode | Codesystem name | Codesystem OID | Description |
| During the morning | 73775008 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | s ochtends |
| During the afternoon | 255213009 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | s middags |
| During the evening | 3157002 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | s avonds |
| During the night | 2546009 | SNOMED CT | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 | s nachts |
This information model in other releases
Information model references
This information model refers to
This information model is used in
Technical specifications in HL7v3 CDA and HL7 FHIR
To exchange information based on health and care information models, additional, more technical specifications are required.
Not every environment can handle the same technical specifications. For this reason, there are several types of technical specifications:
- HL7® version 3 CDA compatible specifications, available through the Nictiz ART-DECOR® environment

- HL7® FHIR® compatible specifications, available through the Nictiz environment on the Simplifier FHIR

Downloads
This information model is also available as pdf file ![]() or as spreadsheet
or as spreadsheet ![]()
About this information
The information in this wikipage is based on Registratie aan de bron publication 2015 including errata dd. 16-07-2015
Conditions for use are located on the mainpage ![]()
This page is generated on 24/12/2018 12:30:32 with ZibExtraction v. 3.0.6932.1989